Introduction
A 409A valuation is the process used to determine the fair market value (FMV) of a private company’s common stock. Mandated by Section 409A of the U.S. Internal Revenue Code, this valuation is particularly significant when setting the strike price for stock options.
For private companies—especially startups—equity-based compensation has become a critical strategy for attracting and retaining top talent. However, issuing stock options comes with regulatory responsibilities, and one of the most essential requirements is obtaining a compliant 409A valuation.
We through this article explores the fundamentals of 409A valuation, highlights its importance, and examines how companies can use it not only to ensure compliance but also to drive long-term strategic growth.
Understanding 409A Valuation
A 409A valuation is an independent assessment that determines the FMV of a private company’s common stock. It is required when issuing nonqualified deferred compensation— such as stock options and RSUs—and ensures that the strike price reflects the stock’s fair value.
Beyond compliance, a well-supported 409A valuation signals sound financial practices and instills trust among investors and employees.
Key points:
- Ensures defensible pricing for equity awards;
- Avoids tax penalties for underpriced stock options;
- Demonstrates financial transparency and fairness.
Private Companies and 409A Valuation
Startups and high-growth private companies often use equity as part of their compensation packages to compete with public companies and attract skilled professionals. In this setup, a 409A valuation becomes more than a legal formality—it’s a practical necessity.
It supports:
- Documented FMV determination based on accepted methodologies;
- IRS “safe harbor” protection, reducing audit risk;
- Proper setting of strike prices for stock options.
Issuing stock options below FMV can trigger significant tax liabilities and penalties, making timely valuations critical.
Why You Need a 409A Valuation for ASC 718
Although Section 409A addresses tax rules, the FMV determined through a 409A valuation is also important for financial reporting under ASC 718. Since private companies lack a public stock price, they rely on this valuation for both compliance and accounting purposes.
A 409A valuation helps companies:
- Set the appropriate exercise price for stock options;
- Determine the grant-date fair value for equity awards under ASC 718;
- Ensure consistency in tax and financial reporting.
When Do You Need to Get a 409A Valuation?
A 409A valuation is required before issuing any form of equity compensation, such as stock options, to employees, advisors, or other stakeholders. For startups, obtaining this valuation isn’t a one-time task—it must be updated annually or sooner if there are material changes that could affect the company’s value.
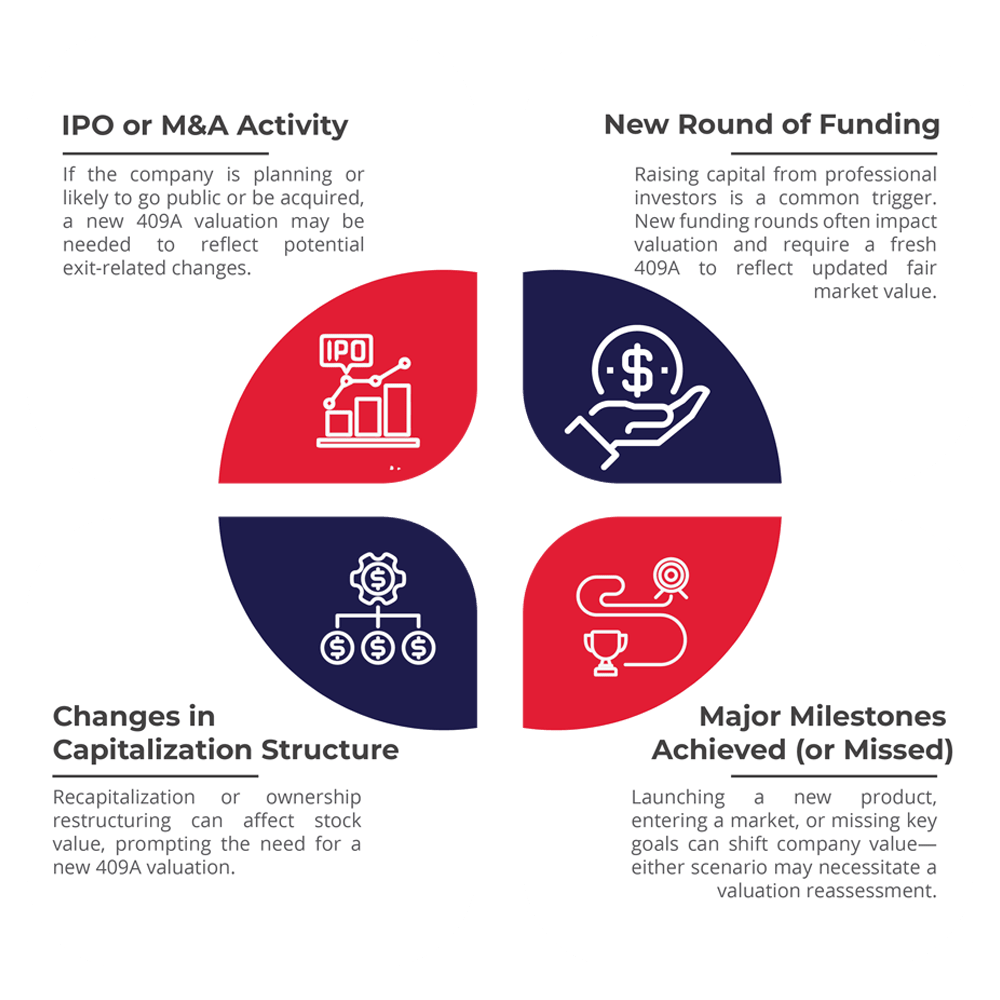
Common Methods Used in 409A Valuation
To ensure compliance with IRS standards and to obtain safe harbor protection, a 409A valuation should be conducted by an independent, qualified appraiser. The appraiser typically selects from three core valuation methodologies to determine the fair market value (FMV) of a private company’s common stock:
1. Market Approach
This approach is commonly used for early-stage startups that may not yet be profitable or lack reliable financial forecasts. It involves comparing the startup to similar publicly traded companies or recent mergers and acquisitions involving comparable businesses. By benchmarking against the market, appraisers derive an estimate of FMV based on external data.
2. Income Approach
Suitable for startups with predictable revenue and positive cash flow, the income approach evaluates the company’s value based on its projected future earnings, often discounted to present value. This method requires a detailed financial forecast and assumes the company’s income-generating ability is a reliable basis for valuation.
3. Asset Approach
This method estimates value based on the net assets of the company—calculated as total assets minus total liabilities. It is often used for early-stage startups that have not yet raised external capital or begun generating revenue, making income-based or market-based models less applicable.
Equity Allocation Models in 409A Valuations
In 409A valuations, particularly for private companies with layered capital structures, choosing the right method to allocate equity value among different share classes is crucial. These models ensure that preferred and common shares are treated fairly, especially in light of liquidation preferences and varying rights. The most widely accepted approaches include the Current Value Method (CVM), Probability-Weighted Expected Return Method (PWERM), Option Pricing Model (OPM), and the Hybrid Method, which blends elements of PWERM and OPM.
Current Value Method (CVM)
CVM is a static approach that assumes the company is sold or liquidated immediately at its current valuation. It allocates value based on the capital structure as of the valuation date, giving priority to preferred shareholders and assigning any residual value to common shareholders. Since it does not account for future performance, this method is typically reserved for very early-stage companies or when a liquidity event is imminent.
- Assumes an immediate sale or liquidation event
- Prioritizes liquidation preferences and existing equity rights
- Not suitable for companies with growth expectations or recent funding rounds Probability-Weighted Expected Return Method (PWERM)
PWERM models various possible exit outcomes—such as an IPO, acquisition, or dissolution—and assigns probabilities to each. The equity value is calculated under each scenario, then discounted and combined based on those probabilities. This method is wellsuited for companies with a reasonably foreseeable exit path, supported by credible internal projections.
- Accounts for multiple potential exit scenarios
- Incorporates company-specific probabilities and timing
- Useful when management can justify assumptions with data
Option Pricing Model (OPM)
The OPM treats each class of stock as a call option on the company’s total equity value. It assumes that value will be realized in the future and allocates it based on thresholds set by liquidation preferences. This method is particularly useful when the timing of exit events is uncertain and the company has a layered capital structure.
- Uses models like Black-Scholes for value simulation
- Ideal for early- and mid-stage companies with no immediate exit
- Sensitive to assumptions like volatility and time to liquidity
Hybrid Method
The Hybrid Method blends PWERM and OPM to offer a comprehensive valuation framework. It is used when a specific exit is likely, but alternative outcomes must still be considered. Typically, PWERM models the expected transaction while OPM handles less predictable fallback scenarios. This dual approach allows companies to reflect both certainty and uncertainty in a single valuation.
- Combines scenario-based and option-based modeling
- Suitable when one exit path is probable, but not guaranteed
- Offers flexibility while requiring careful documentation of assumptions
409A Penalties
Failing to comply with the IRS requirements for a 409A valuation—particularly by not using an IRS-approved valuation method or not engaging a qualified appraiser—can disqualify your company from safe harbor protection. This can result in severe tax consequences, especially for employees and shareholders who receive equity-based compensation.
If a 409A valuation is deemed non-compliant, the penalties may include:
- Immediate taxation of all deferred compensation, including equity grants, from the current and prior tax years.
- Accrued interest on the amount deemed taxable.
- An additional 20% penalty tax on the total deferred compensation amount.
While the IRS may not audit every startup, the risk of scrutiny increases significantly as the company matures, especially during critical events like a merger, acquisition, or IPO. A non-compliant 409A valuation can become a major red flag in due diligence processes and may derail transactions.
To mitigate these risks, it’s strongly recommended to engage a reputable and experienced valuation firm from the outset. Doing so not only ensures compliance but also protects your company and its stakeholders from unexpected financial liabilities.
Conclusion
A 409A valuation is a critical requirement for any private company offering equity-based compensation. It provides an independent, IRS-compliant assessment of the company’s fair market value (FMV)—ensuring that the strike price for stock options is set accurately and legally. By doing so, it safeguards both the company and its employees from costly tax penalties and potential legal complications resulting from mispriced equity.
Throughout this article, we’ve explored the importance of 409A valuations, the regulatory framework of IRC Section 409A, and the key triggers that necessitate a revaluation. We also examined the three primary methodologies used to conduct these valuations—market, income, and asset approaches—each suited to different business stages and financial profiles.
To maintain compliance and support long-term growth, companies should:
- Update valuations regularly, especially after significant financial or structural events;
- Engage qualified, independent appraisers;
- Involve legal and financial advisors;
- And balance market competitiveness with regulatory requirements.
By prioritizing a robust 409A valuation process, organizations not only meet legal obligations but also build credibility with investors, trust with employees, and a foundation for strategic decision-making. In essence, a well-executed 409A valuation is more than a compliance formality—it’s a strategic asset that supports sustainable and transparent growth.
